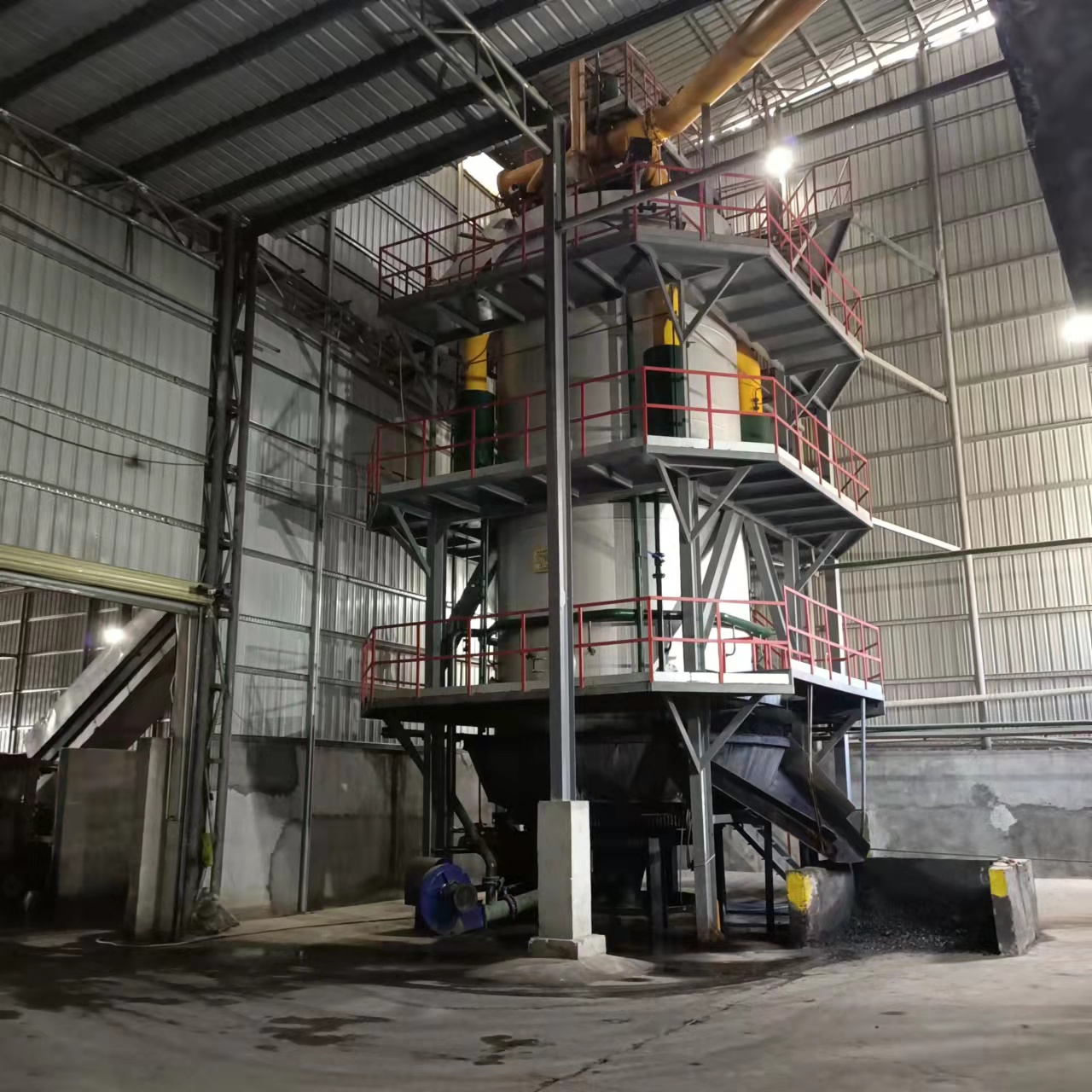
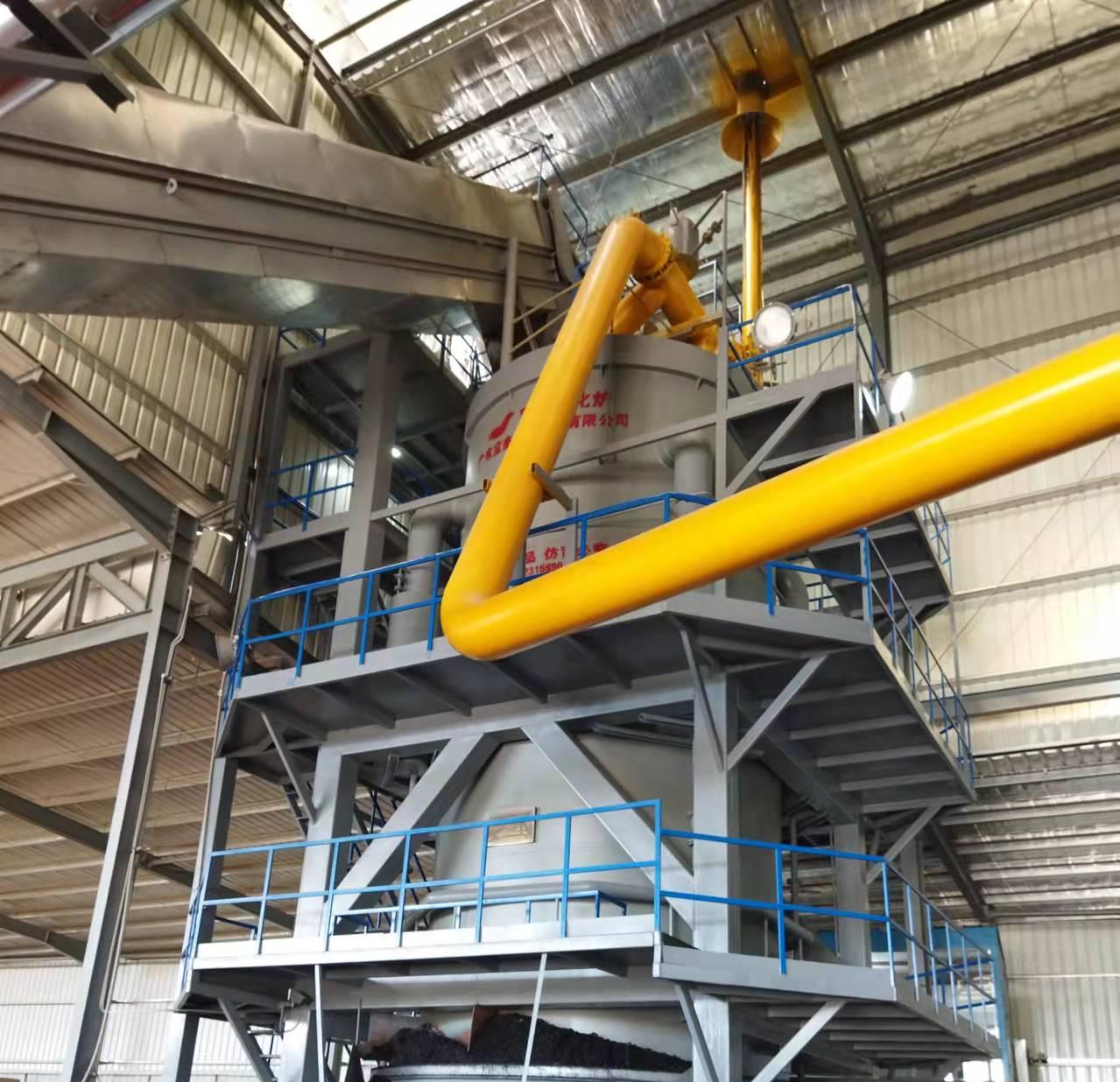
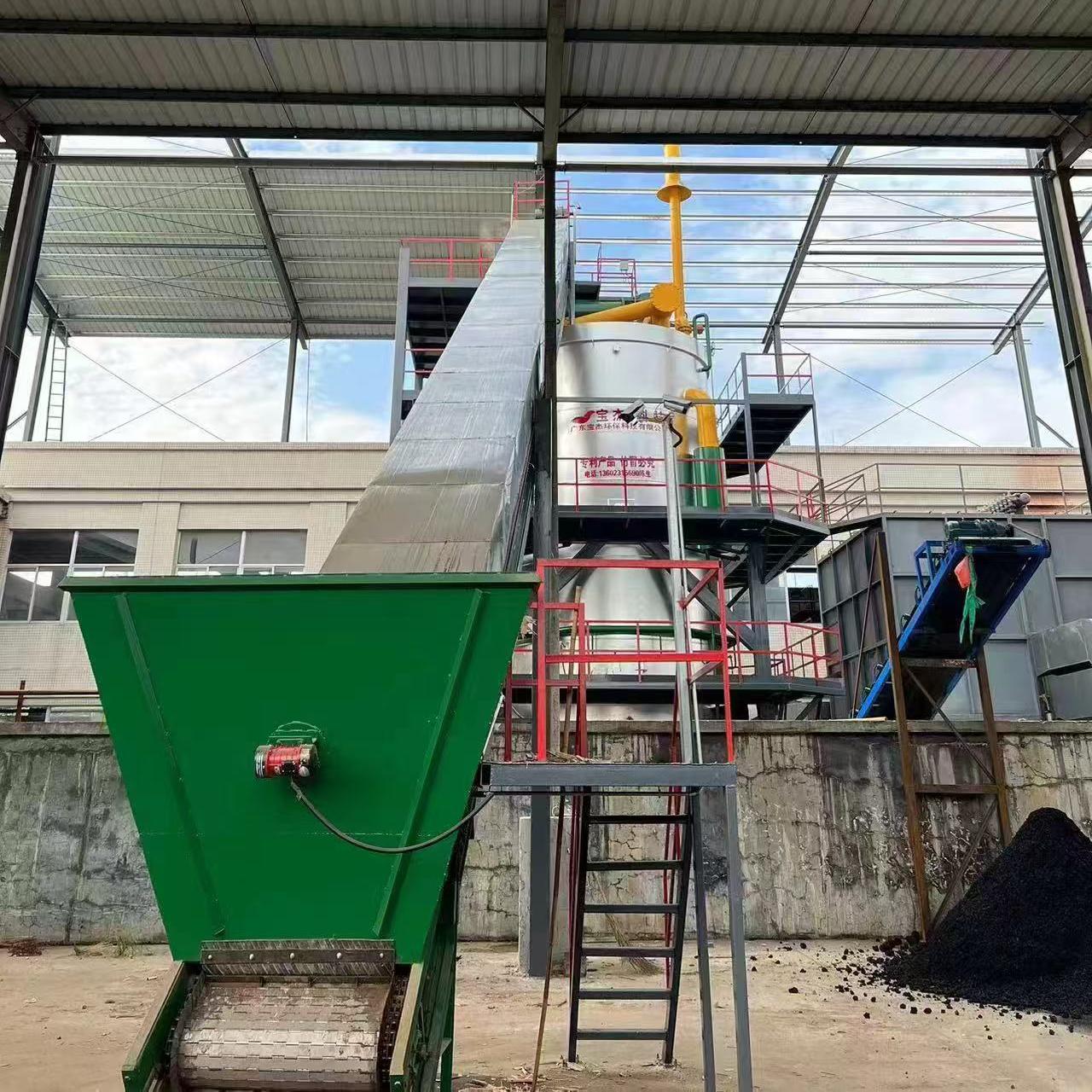
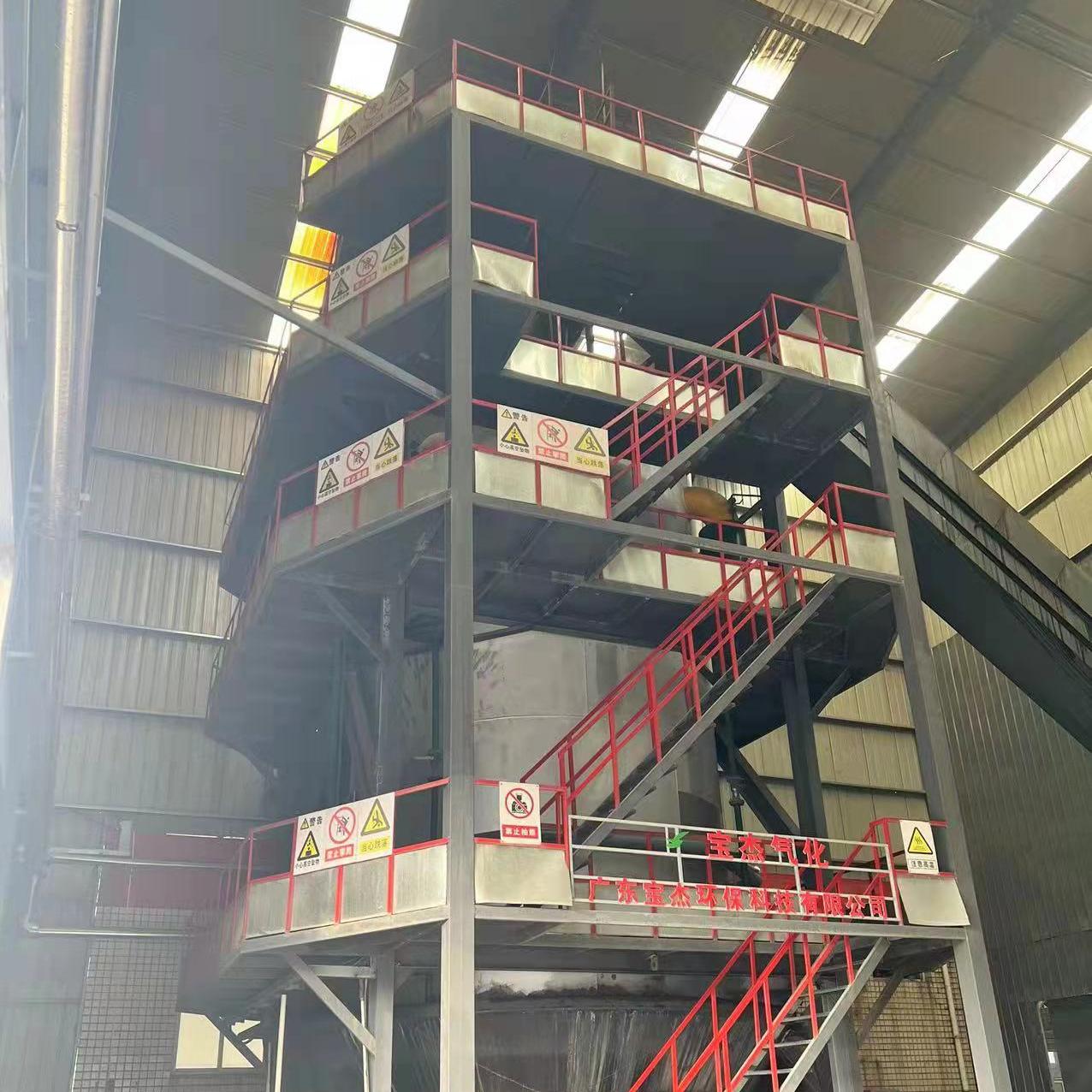
R&D and manufacture of biomass gasification equipment, environmental protection equipment, boiler equipment, investment in heating (steam) energy operation and management.
Tel:+86 0769-82928980
E-mail:[email protected]
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
Industry News
Biomass Gas Boilers: Sustainable Heating Solutions for the Future
As the world moves towards more sustainable energy solutions, the demand for renewable energy sources continues to rise. One of the most promising technologies in the realm of renewable energy is the biomass gas boiler, which harnesses organic materials to generate heat and electricity in an environmentally friendly way. Biomass boilers are gaining traction as a sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuel-based heating systems, offering significant benefits in terms of energy efficiency, cost savings, and environmental impact.
The process begins with the biomass feedstock, which can include wood chips, sawdust, agricultural waste (like straw or corn cobs), or even municipal solid waste. The feedstock is placed in the gasifier, where it undergoes a process of heating in a low-oxygen environment.
During gasification, the biomass is heated to high temperatures, usually between 700°C and 900°C, which causes the organic material to break down into gases like methane, carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and other volatile compounds. This process occurs in a sealed chamber, which limits the amount of oxygen, preventing full combustion and allowing the organic material to convert into a combustible gas.
The gas produced by the gasifier is then cleaned of impurities such as tar, ash, and particulates. This cleaning process is essential to ensure that the gas is suitable for burning in the boiler, as impurities can damage the system and reduce efficiency.
The cleaned gas is then fed into the combustion chamber of the boiler, where it is ignited and burned to generate heat. The heat produced is transferred to the water in the boiler, which then circulates through pipes to provide hot water or space heating for buildings.
In addition to heating, some biomass gas boilers can also be used to generate electricity, making them an ideal solution for combined heat and power (CHP) applications. The excess heat produced in the gasification and combustion process can be used for power generation, further improving the overall efficiency of the system.
One of the main reasons biomass gas boilers are gaining popularity is their sustainability. Biomass is a renewable energy source, unlike fossil fuels such as coal or natural gas, which are finite. Biomass comes from organic materials that can be replenished through sustainable agricultural practices, making it a more eco-friendly option for heating.

Biomass gas boilers emit significantly less carbon dioxide compared to traditional fossil fuel-based boilers. When biomass is burned, the carbon released is part of the natural carbon cycle, as plants absorb carbon dioxide during their growth. This contrasts with burning fossil fuels, which release carbon that has been stored underground for millions of years, contributing to the greenhouse effect and global warming.Although the initial installation of a biomass gas boiler can be more expensive than conventional heating systems, the long-term cost savings are considerable. Biomass fuel is often cheaper than oil or natural gas, particularly in regions where biomass resources are abundant. Additionally, biomass boilers have a longer lifespan than conventional gas boilers, which further enhances their cost-effectiveness.
Biomass gas boilers can help reduce dependency on imported fuels, providing greater energy security. In areas where biomass is locally sourced, individuals and businesses can become more self-reliant in their energy needs. This is particularly important for countries looking to reduce their reliance on foreign oil or gas imports.
Biomass gas boilers offer great flexibility in terms of the types of fuel that can be used. Depending on availability, different types of biomass can be burned, including wood pellets, chips, agricultural waste, and even waste products from industries. This flexibility makes biomass gas boilers suitable for a wide range of applications and geographic locations.
Biomass gas boilers are designed to be durable and require relatively low maintenance. The gasification process itself minimizes the amount of particulate matter and ash produced, reducing the need for frequent cleaning and maintenance. However, like any heating system, regular servicing is necessary to ensure optimal performance.
In homes, biomass gas boilers are an excellent alternative to traditional heating systems, especially in rural or off-grid areas. They provide an eco-friendly and cost-effective solution for heating water and space, while also offering the option to use locally sourced biomass fuel. This can be particularly beneficial in areas where other forms of heating are expensive or unavailable.
Many businesses and industrial facilities are turning to biomass gas boilers for their heating and energy needs. These systems are ideal for large-scale applications, such as factories, warehouses, and district heating systems, where they can supply heat to multiple buildings or areas. Biomass gas boilers can also be integrated into combined heat and power (CHP) systems, allowing businesses to generate electricity in addition to heat.
Biomass gas boilers are increasingly being used in district heating systems, which provide centralized heating to a network of homes, buildings, or even entire communities. These systems are highly efficient and reduce the need for individual heating systems in each building, offering cost savings and a reduction in carbon emissions across a large area.
Agricultural businesses can benefit from biomass gas boilers by using agricultural waste products, such as crop residues, to fuel the system. In addition to providing heating for greenhouses, barns, or other agricultural buildings, biomass gas boilers can be used to power equipment or generate electricity, further enhancing the sustainability of farming operations.
While biomass gas boilers offer numerous advantages, there are some challenges to consider:
The upfront cost of a biomass gas boiler system can be higher than traditional gas or oil heating systems. However, the long-term savings in fuel costs and the environmental benefits often justify the investment.
The availability of biomass fuel can vary by region. In areas where biomass resources are scarce, the cost of fuel may be higher, potentially affecting the overall economics of the system.
Biomass gas boilers require a sufficient amount of space for both the boiler itself and the storage of fuel. In urban areas with limited space, this could pose a challenge.
Quick Links
Products
contact Us
 Tel: +86 0769-82928980
Tel: +86 0769-82928980 Fax: [email protected]
Fax: [email protected] E-mail: [email protected]
E-mail: [email protected] Company Address: Dalang Chamber of Commerce Building, No. 288 Yinlang South Road, Dalang Town, Dongguan City 13333, China
Company Address: Dalang Chamber of Commerce Building, No. 288 Yinlang South Road, Dalang Town, Dongguan City 13333, China Factory Add:
West side of Centre Road and south side of Zhongyuan Road within Hongcaoyuan, Hongcao Town, Shanwei Urban District
Factory Add:
West side of Centre Road and south side of Zhongyuan Road within Hongcaoyuan, Hongcao Town, Shanwei Urban District
Copyright© 2022 Guangdong Bao Jie Technology Co., Ltd.All Rights Reserved.


 EN
EN 





