R&D and manufacture of biomass gasification equipment, environmental protection equipment, boiler equipment, investment in heating (steam) energy operation and management.
Tel:+86 0769-82928980
E-mail:[email protected]
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
Industry News
How Can Biomass Gasifier Contribute to Sustainable and Renewable Energy Solutions?
As the world shifts towards more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy solutions, biomass gasification has emerged as a promising technology. A biomass gasifier is a device that converts organic materials into clean energy, offering an alternative to fossil fuels and contributing to the reduction of carbon emissions. This process plays a significant role in the transition to renewable energy by utilizing locally available biomass resources to produce power, heat, and fuels.
The biomass gasification process typically involves three stages:
Drying: Biomass moisture is evaporated through heat.
Pyrolysis: The biomass is decomposed at high temperatures to produce volatile gases and charcoal.
Gasification: The volatile gases react with limited oxygen or steam to produce syngas, which can then be used for energy production.
Biomass is a renewable resource, as it is derived from organic materials that can be replenished through agriculture, forestry, and waste management. Biomass gasifiers offer an alternative to finite fossil fuels, making them a crucial component of sustainable energy systems.
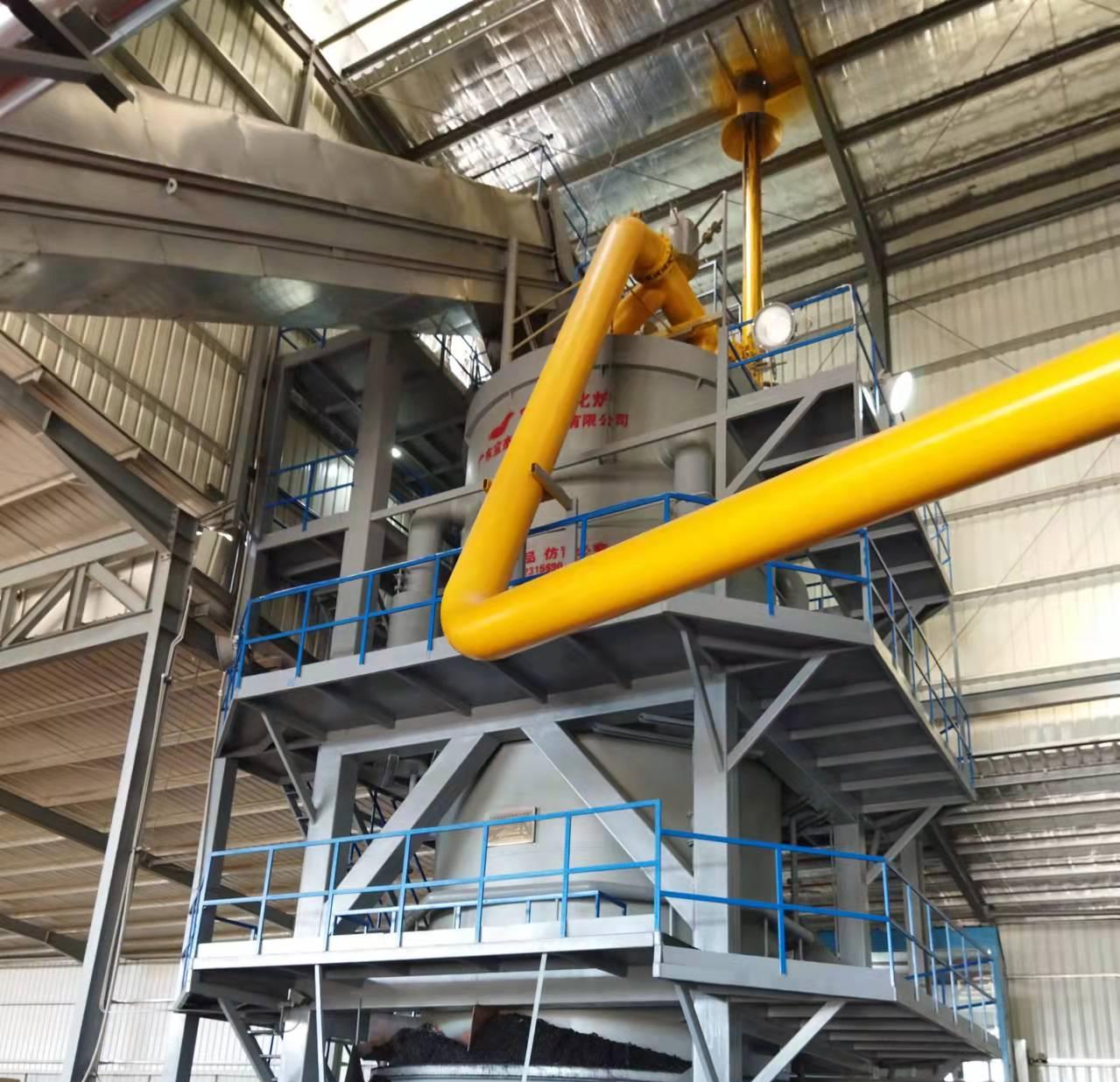

Biomass gasification produces far fewer greenhouse gases compared to fossil fuel combustion. Since biomass is carbon-neutral (the carbon released during combustion is offset by the carbon absorbed during plant growth), it offers an environmentally friendly alternative to traditional energy sources.
Biomass gasifiers can utilize a variety of organic waste materials, including agricultural residues, forestry waste, and municipal solid waste. This provides an effective method for reducing waste and converting it into useful energy, addressing both energy and waste management issues.
By using locally available biomass materials, countries and communities can reduce their dependence on imported fossil fuels, leading to greater energy security and reduced vulnerability to global energy price fluctuations.
Biomass gasifiers offer a cost-effective energy solution, especially in rural and agricultural areas where biomass resources are abundant. The initial investment in a biomass gasifier can be offset by long-term savings on energy costs, making it an attractive option for both industrial and small-scale applications.
The syngas produced by biomass gasifiers can be used for various purposes, including electricity generation, heating, and the production of biofuels like ethanol and methane. This versatility makes biomass gasifiers adaptable to a wide range of energy needs.
Biomass gasifiers are often used in combined heat and power (CHP) plants to generate electricity. The syngas is burned in a gas turbine or engine to produce power, while the heat generated can be used for industrial processes or district heating.
Biomass gasification is widely used in industries such as paper, food processing, and textiles, where heat is required for manufacturing processes. Gasifiers provide a reliable and cost-effective source of heat, reducing the reliance on conventional fuels like coal and natural gas.
Syngas produced from biomass can be further processed to produce biofuels such as methanol, ethanol, and biodiesel. These biofuels can be used in transportation, providing an alternative to gasoline and diesel.
Biomass gasifiers can also be used in small-scale applications, such as rural electrification, where they provide power to communities that are not connected to the main power grid.
Biomass gasifiers play a significant role in waste-to-energy projects by converting organic waste into syngas, which can then be used to generate electricity or heat. This not only reduces waste but also provides a sustainable source of energy.
While biomass gasifiers are cost-effective in the long term, the initial setup cost can be relatively high. The purchase and installation of a gasification unit, along with infrastructure for collecting and processing biomass, may be a barrier for some communities or businesses.
The availability and quality of biomass feedstock can vary depending on location, weather conditions, and agricultural practices. Consistency in feedstock supply and quality is crucial for the efficient operation of a biomass gasifier.
Biomass gasification systems require specialized knowledge for design, operation, and maintenance. In regions with limited technical expertise, the efficient operation of a gasifier can be challenging.
While biomass gasification produces fewer emissions compared to traditional combustion, it is not completely free of pollutants. Syngas contains trace amounts of particulate matter, carbon monoxide, and nitrogen oxides, which need to be managed with proper filtration and cleaning systems.
Biomass gasification represents a sustainable and versatile solution for renewable energy production. By converting organic waste materials into valuable energy, biomass gasifiers address multiple challenges, including waste management, energy security, and environmental sustainability. While there are challenges to be overcome, such as high initial costs and feedstock availability, the benefits of biomass gasification make it a promising technology in the global shift towards cleaner energy systems. As technology advances and efficiency improves, biomass gasifiers will play an increasingly vital role in the renewable energy landscape.
Quick Links
Products
contact Us
 Tel: +86 0769-82928980
Tel: +86 0769-82928980 Fax: [email protected]
Fax: [email protected] E-mail: [email protected]
E-mail: [email protected] Company Address: Dalang Chamber of Commerce Building, No. 288 Yinlang South Road, Dalang Town, Dongguan City 13333, China
Company Address: Dalang Chamber of Commerce Building, No. 288 Yinlang South Road, Dalang Town, Dongguan City 13333, China Factory Add:
West side of Centre Road and south side of Zhongyuan Road within Hongcaoyuan, Hongcao Town, Shanwei Urban District
Factory Add:
West side of Centre Road and south side of Zhongyuan Road within Hongcaoyuan, Hongcao Town, Shanwei Urban District
Copyright© 2022 Guangdong Bao Jie Technology Co., Ltd.All Rights Reserved.


 EN
EN 





