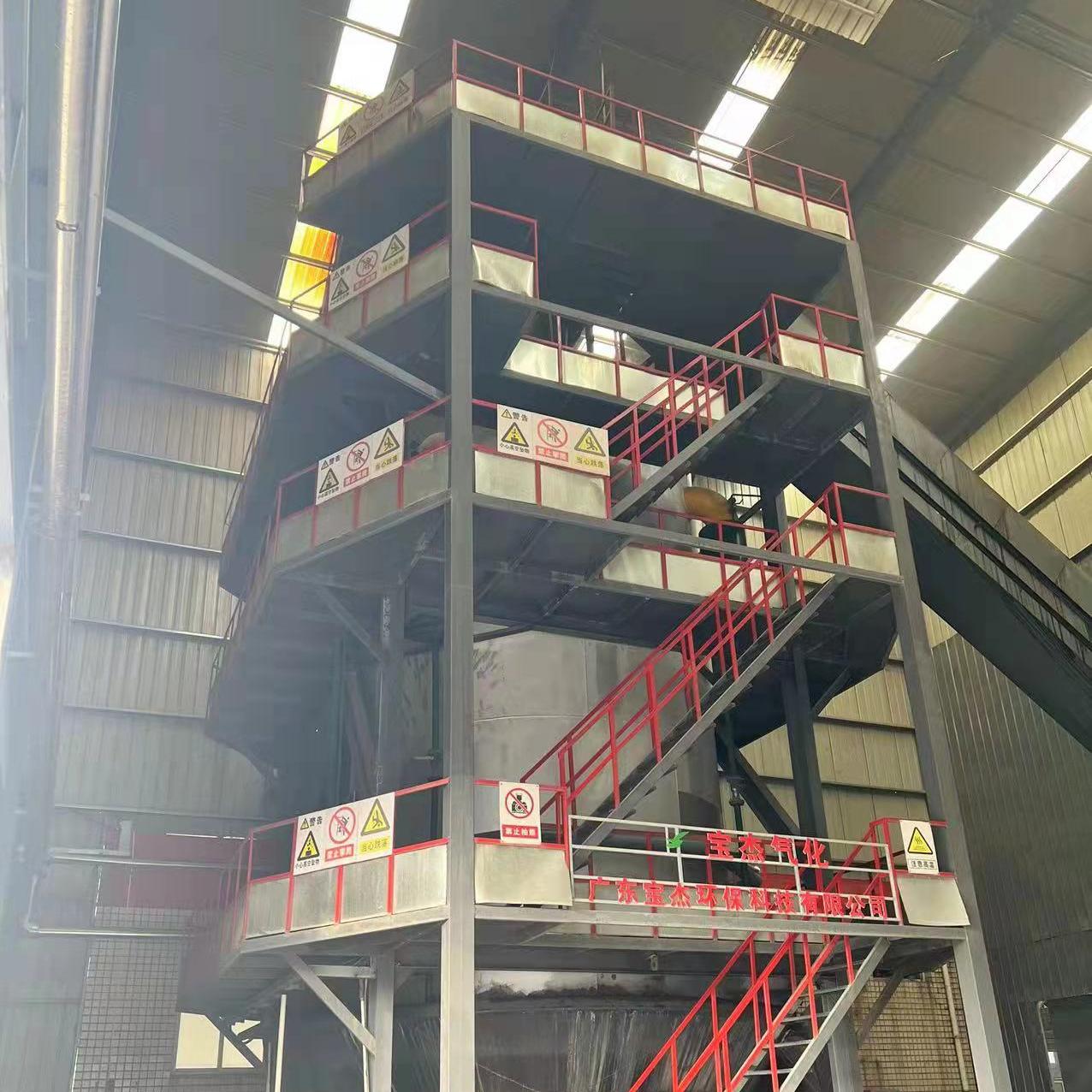
R&D and manufacture of biomass gasification equipment, environmental protection equipment, boiler equipment, investment in heating (steam) energy operation and management.
Tel:+86 0769-82928980
E-mail:[email protected]
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
Industry News
Biomass Gas Boiler: An Eco-Friendly Heating Solution
As the world increasingly turns towards renewable energy solutions to combat climate change, biomass energy is emerging as a sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuels. One of the key technologies enabling this shift is the biomass gas boiler, an environmentally friendly system that utilizes organic materials to produce heat and power.
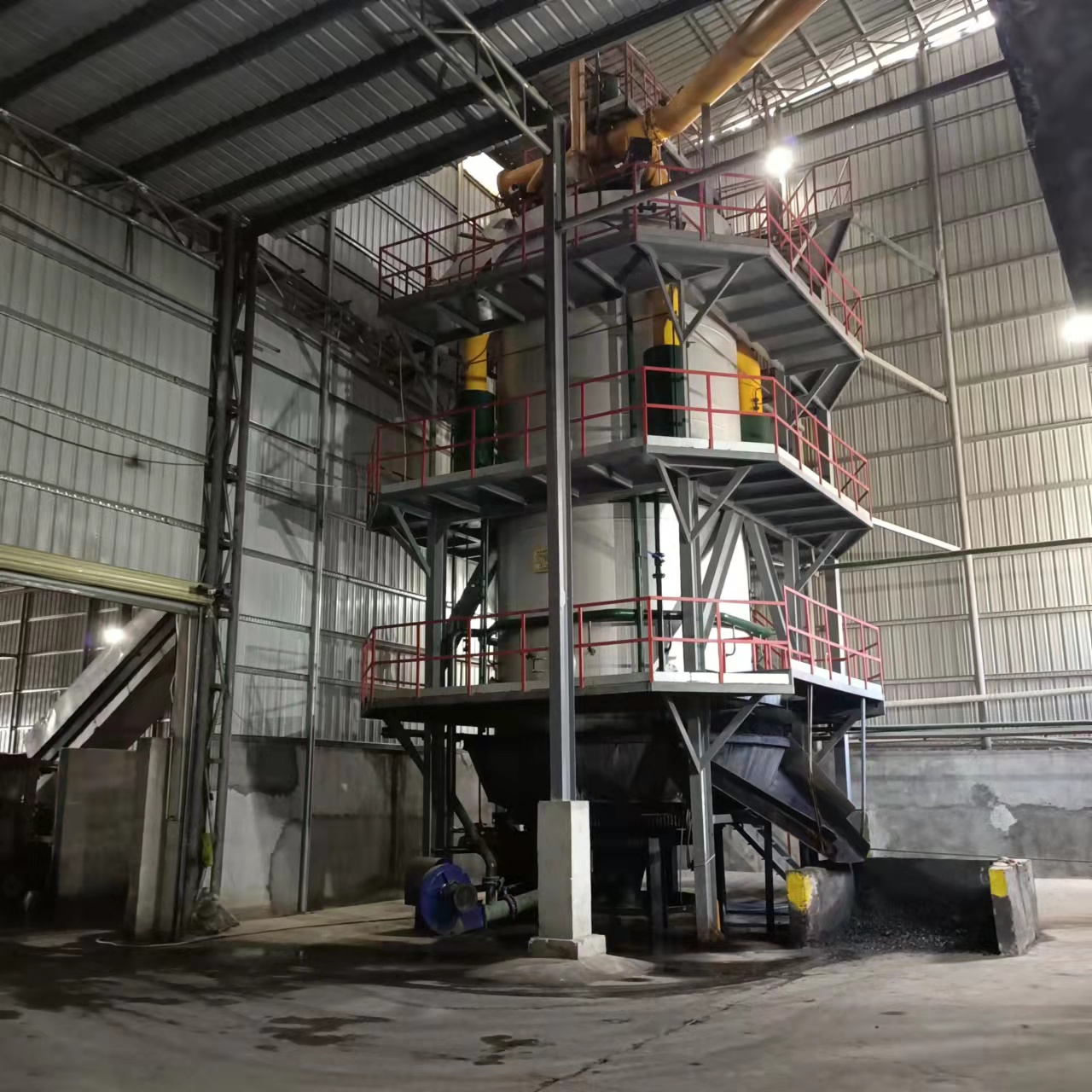
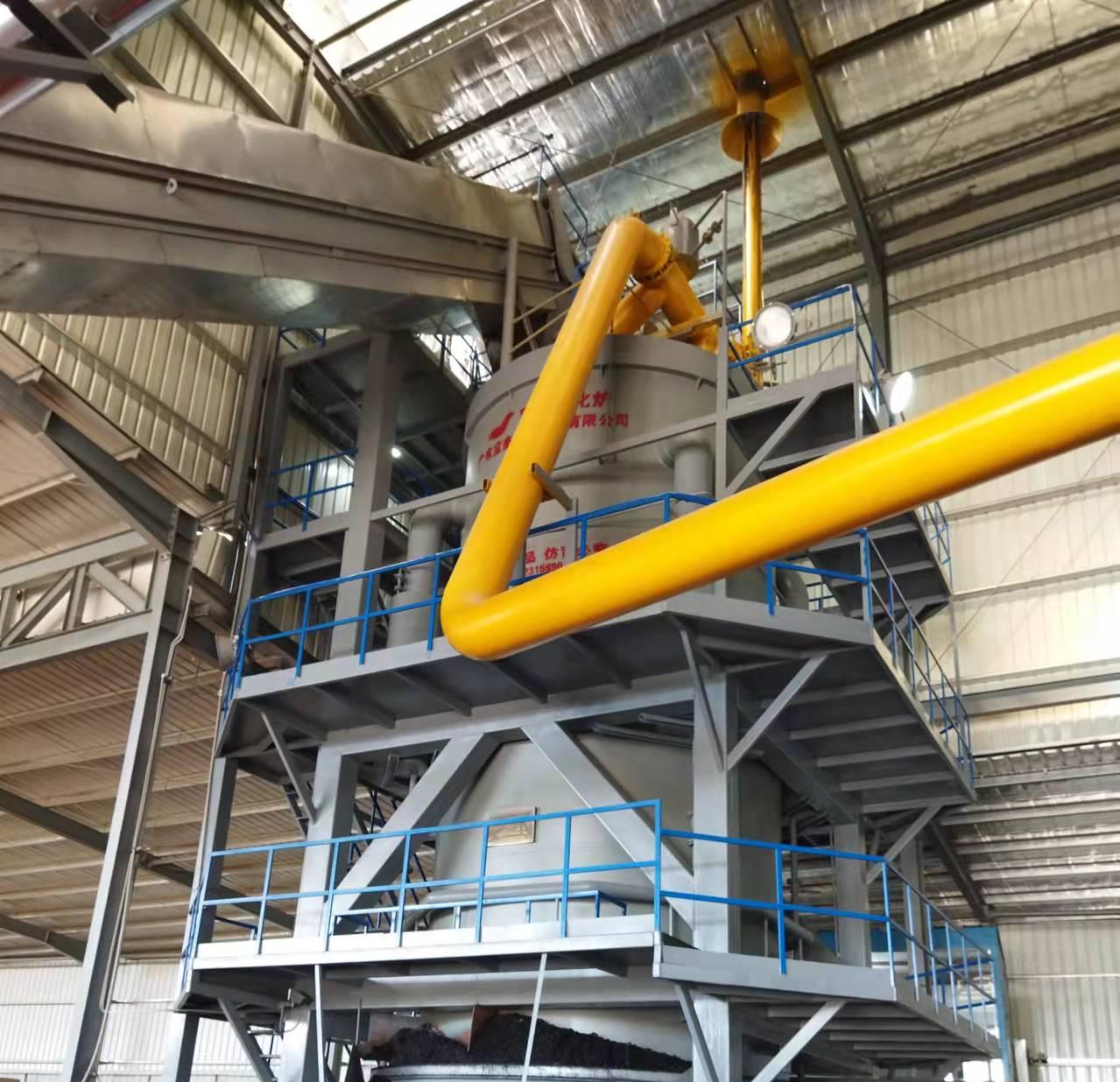
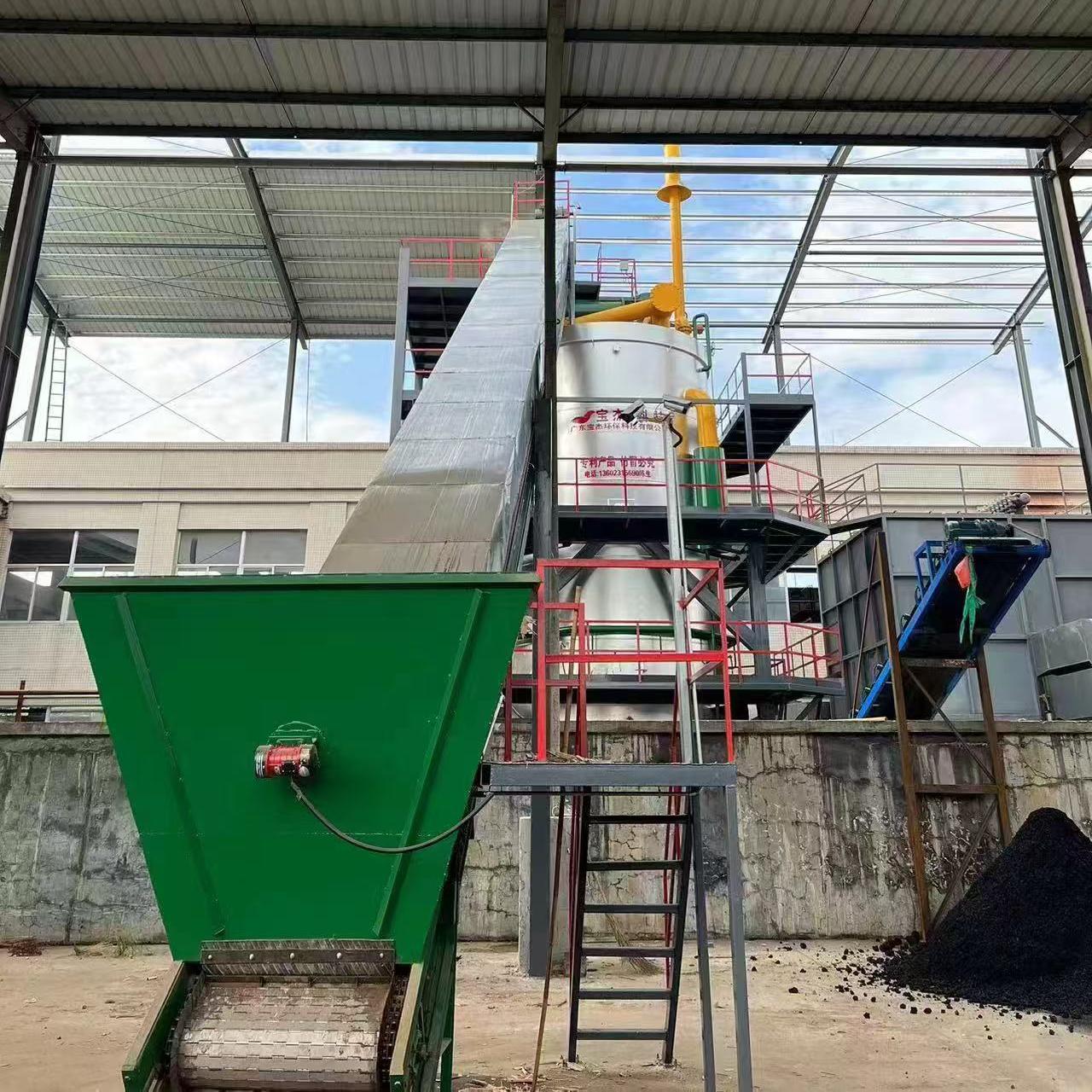
A biomass gas boiler is a heating system that uses organic materials—often referred to as biomass—to generate heat through a process called gasification. Biomass materials include wood chips, pellets, agricultural residues, or other plant-based organic matter. These materials are converted into biogas (mainly methane) by heating them in a low-oxygen environment, a process that produces clean, renewable energy. The gas is then used to fuel a boiler, which heats water or air for residential, industrial, or commercial use.
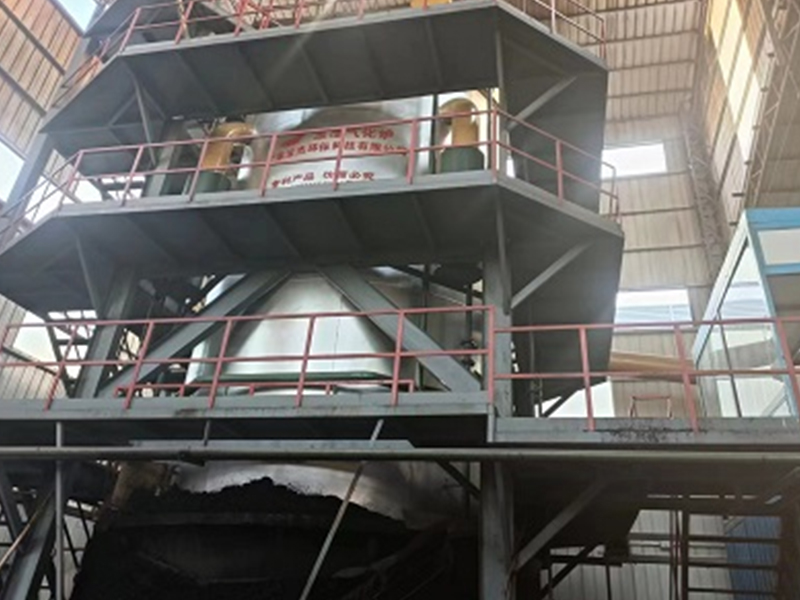

In contrast to traditional boilers that burn solid biomass directly, a biomass gas boiler relies on the gasification process to create a cleaner, more efficient combustion process. The result is a lower environmental impact compared to conventional heating methods.
Biomass materials, such as wood pellets, sawdust, or agricultural waste, are loaded into the gasifier chamber. This chamber is designed to operate under controlled conditions, with limited oxygen supply.
The biomass is heated to high temperatures, typically between 700-900°C, in the gasifier. The heat causes the biomass to break down, releasing volatile gases and leaving behind solid charcoal or ash. The released gases mainly consist of carbon monoxide, methane, and hydrogen.
The produced gas is filtered to remove any impurities such as tar or ash particles. This ensures that only clean, usable gas enters the boiler’s combustion chamber.
The cleaned gas is then directed to the combustion chamber of the boiler, where it is ignited. The heat generated by this combustion process is transferred to water or air, depending on the system’s design. The heated water or air is circulated to provide space heating, hot water, or even to power steam turbines for electricity generation.
After combustion, the remaining byproducts (such as ash or slag) are safely removed from the system, ensuring minimal waste generation.
Biomass is considered a renewable resource because it is derived from organic matter that can be replenished annually. By using biomass for heating, we can reduce our reliance on non-renewable fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas, contributing to a cleaner, greener future.
One of the significant advantages of biomass gas boilers is that they are considered carbon neutral. The carbon dioxide released during the combustion of biomass is offset by the carbon absorbed by the plants during their growth phase. This creates a closed carbon loop, helping to reduce overall greenhouse gas emissions.
Biomass materials, such as agricultural residues or wood waste, are often byproducts that would otherwise go to landfills or be burned in open air. By converting this waste into energy, biomass gas boilers help divert waste from landfills and reduce pollution.
Biomass gasification systems are highly efficient. By producing clean, high-energy gas for combustion, biomass gas boilers can achieve better thermal efficiency compared to traditional biomass boilers that burn solid materials directly. This translates into lower fuel consumption and lower operating costs.
Using locally sourced biomass for heating can help reduce dependency on imported fossil fuels, providing greater energy security. For businesses and homeowners, this can also translate into lower heating costs over time.
In rural or off-grid areas, biomass gas boilers are increasingly used for residential heating. Homeowners can use wood pellets or other biomass materials to fuel the system, providing a cost-effective and sustainable alternative to traditional heating methods.
Biomass gas boilers are widely used in industries such as agriculture, paper production, and food processing. These industries often generate large quantities of organic waste, which can be used as a biomass feedstock for gasification. Biomass boilers can provide a reliable and affordable source of heat for industrial operations.
Biomass gas boilers are also used in district heating systems, where a central boiler provides heat to multiple buildings or homes in a specific area. These systems are particularly effective in urban or suburban regions, offering a cleaner, more sustainable alternative to natural gas or coal-fired district heating plants.
In some large-scale applications, biomass gasifiers are used to generate electricity. The gas produced during gasification can be used to power a steam turbine, which drives an electrical generator. This is particularly useful in industrial settings where both heat and power are required.
Quick Links
Products
contact Us
 Tel: +86 0769-82928980
Tel: +86 0769-82928980 Fax: [email protected]
Fax: [email protected] E-mail: [email protected]
E-mail: [email protected] Company Address: Dalang Chamber of Commerce Building, No. 288 Yinlang South Road, Dalang Town, Dongguan City 13333, China
Company Address: Dalang Chamber of Commerce Building, No. 288 Yinlang South Road, Dalang Town, Dongguan City 13333, China Factory Add:
West side of Centre Road and south side of Zhongyuan Road within Hongcaoyuan, Hongcao Town, Shanwei Urban District
Factory Add:
West side of Centre Road and south side of Zhongyuan Road within Hongcaoyuan, Hongcao Town, Shanwei Urban District
Copyright© 2022 Guangdong Bao Jie Technology Co., Ltd.All Rights Reserved.


 EN
EN 





