R&D and manufacture of biomass gasification equipment, environmental protection equipment, boiler equipment, investment in heating (steam) energy operation and management.
Tel:+86 0769-82928980
E-mail:[email protected]
Web Menu
Product Search
Exit Menu
Industry News
Biomass Gasifier: An Innovative Solution for Sustainable Energy Production
In today’s world, the demand for renewable energy sources is higher than ever, with the need to reduce carbon emissions and dependence on fossil fuels becoming increasingly urgent. One promising solution to this problem is the biomass gasifier, a technology that converts organic materials into usable energy, particularly in the form of gas for heating, electricity generation, and even transportation fuel. Biomass gasifiers offer a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to conventional energy sources, helping both industries and households achieve greater energy independence while minimizing their environmental footprint.
A biomass gasifier is a device that uses thermochemical processes to convert organic materials such as wood, agricultural waste, food scraps, or dedicated energy crops into a synthetic gas known as syngas (synthesis gas). The gasification process involves heating biomass in an oxygen-limited environment, breaking down the organic matter into gases like carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H₂), and methane (CH₄), while leaving behind solid residues like ash.
The syngas produced can then be used to generate heat, produce electricity, or as a feedstock for other industrial processes, such as the production of biofuels. Unlike combustion, which directly burns biomass to release heat and energy, gasification provides a more efficient method of extracting energy, as it allows for the production of cleaner gases with fewer emissions.
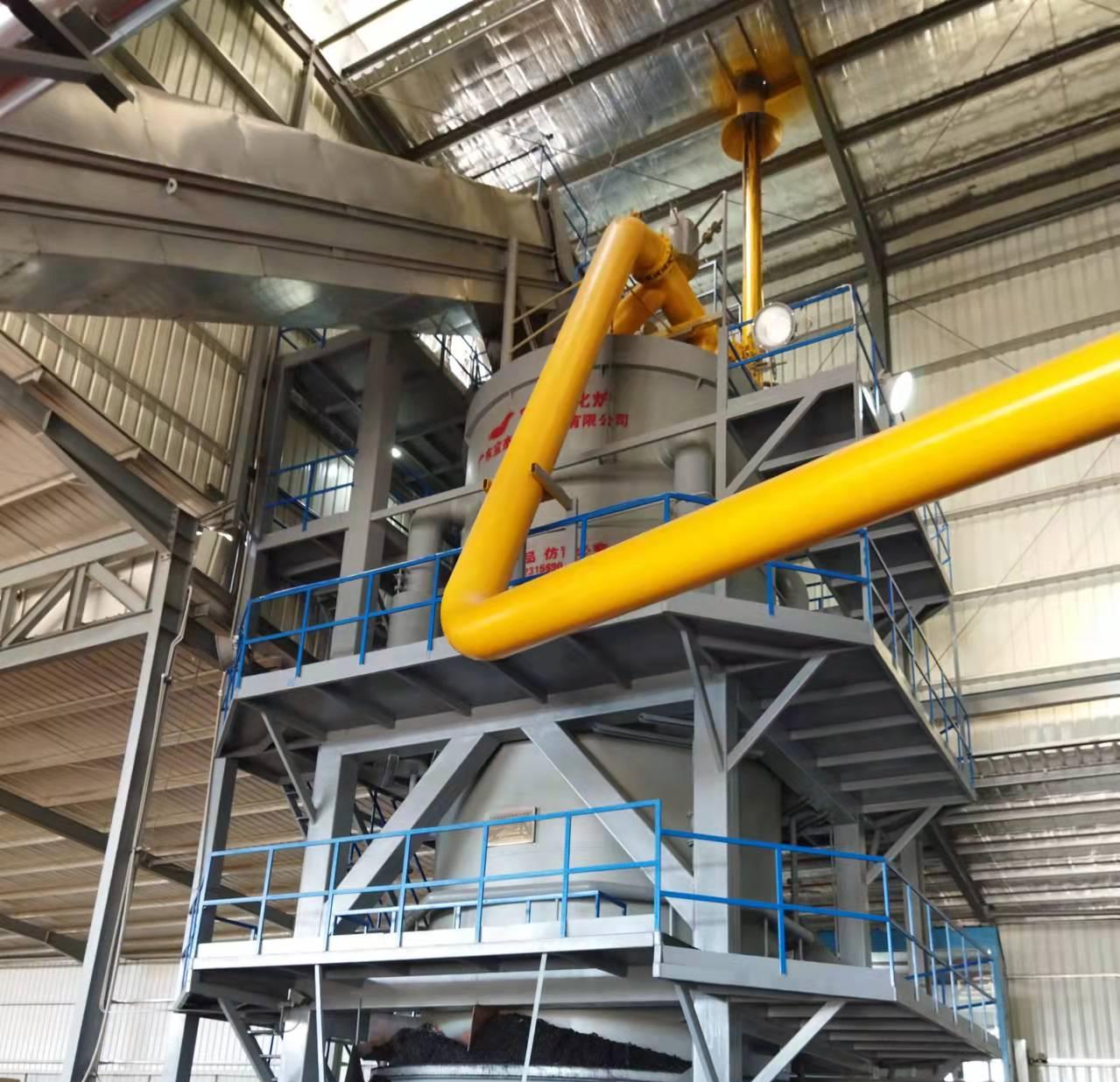

Biomass gasification involves several stages, each critical to the conversion of organic matter into usable energy:
Drying: In the first stage, the biomass material is dried to reduce its moisture content. This is necessary because high moisture levels can hinder the efficiency of the gasification process.
Pyrolysis: Once the biomass is sufficiently dried, it undergoes pyrolysis, a process in which the material is heated in the absence of oxygen. This decomposes the biomass into solid char, liquid tar, and volatile gases.
Gasification: The next stage involves subjecting the volatile gases to higher temperatures (around 700-1,000°C) in the presence of a limited amount of oxygen or air. This causes the gases to break down into simpler molecules, including carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and methane, which constitute syngas.
Cooling and Cleaning: The syngas is then cooled and cleaned to remove impurities such as tar, particulates, and ash. This step is essential to prevent damage to engines or turbines used for power generation.
Energy Utilization: Finally, the clean syngas can be used in a variety of applications, including electricity generation via internal combustion engines or gas turbines, heating, or as a substitute for natural gas in industrial processes.
Renewable Energy Source: Biomass gasifiers provide a sustainable method of energy production, utilizing organic waste materials that would otherwise contribute to landfills. Biomass is a renewable resource, as plants and organic materials can be regrown, making it an environmentally friendly alternative to finite fossil fuels.
Reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Biomass gasification has a lower carbon footprint compared to conventional fossil fuels. While biomass does release carbon dioxide when it is converted to energy, the process is considered carbon-neutral because the plants from which the biomass is derived absorbed CO₂ during their growth. Additionally, the syngas produced from biomass is cleaner than burning coal or natural gas, reducing the release of harmful pollutants like sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides.
Waste Management: Biomass gasifiers play an essential role in waste management by converting agricultural residues, forestry waste, food scraps, and even municipal solid waste into valuable energy. This reduces the amount of organic waste that ends up in landfills, where it would otherwise decompose anaerobically and release methane, a potent greenhouse gas.
Energy Independence: By utilizing locally available biomass materials, individuals, communities, and industries can generate their own energy, reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels. This is particularly beneficial for rural areas or off-grid communities where access to traditional energy sources may be limited.
Versatility and Flexibility: Biomass gasifiers can be used for a wide range of applications. They can provide electricity and heat for homes and businesses, power industrial processes, or even be converted into biofuels for vehicles. This versatility makes biomass gasification an attractive solution for diverse energy needs, from small-scale domestic use to large industrial applications.
Economic Opportunities: Biomass gasification can stimulate local economies by creating jobs in the collection, processing, and conversion of biomass. In rural areas, where biomass materials like agricultural residues are abundant, gasifiers can create new economic opportunities by supporting local energy production and waste management efforts.
Biomass gasifiers are employed in various sectors, demonstrating their adaptability and usefulness:
Electricity Generation: Many biomass gasifiers are used in power plants to generate electricity. By converting biomass into syngas, which is then used to power gas turbines or engines, biomass can contribute to the electricity grid, especially in remote areas or developing countries where access to conventional electricity infrastructure is limited.
Cogeneration: Biomass gasifiers are also used in combined heat and power (CHP) systems, where both electricity and heat are produced simultaneously. This can be particularly useful for industrial facilities that require both power and heat for manufacturing processes, such as food processing or chemical production.
Biofuels Production: The syngas produced in a biomass gasifier can be converted into biofuels like ethanol or biodiesel, which can be used as renewable alternatives to gasoline and diesel. This application is of great interest in the transportation sector, as it offers a cleaner, more sustainable fuel source.
Rural and Off-Grid Energy: In areas without access to a reliable grid, small-scale biomass gasifiers can be used to generate electricity for individual homes or communities. These systems can run on locally sourced biomass, providing an affordable and independent energy source.
While biomass gasification offers numerous advantages, there are challenges to its widespread adoption. The technology can be costly to set up, particularly for small-scale operations, and the biomass materials themselves must be handled and processed efficiently to ensure optimal gasification performance. Additionally, the need for regular maintenance and the cleaning of syngas can pose operational challenges.
Despite these obstacles, the future of biomass gasifiers looks promising. As technology continues to improve and costs decrease, biomass gasifiers have the potential to play a significant role in the transition to a sustainable energy future. By harnessing the power of organic waste materials, biomass gasifiers offer a clean, renewable, and economically viable solution for meeting the world’s growing energy needs.
Quick Links
Products
contact Us
 Tel: +86 0769-82928980
Tel: +86 0769-82928980 Fax: [email protected]
Fax: [email protected] E-mail: [email protected]
E-mail: [email protected] Company Address: Dalang Chamber of Commerce Building, No. 288 Yinlang South Road, Dalang Town, Dongguan City 13333, China
Company Address: Dalang Chamber of Commerce Building, No. 288 Yinlang South Road, Dalang Town, Dongguan City 13333, China Factory Add:
West side of Centre Road and south side of Zhongyuan Road within Hongcaoyuan, Hongcao Town, Shanwei Urban District
Factory Add:
West side of Centre Road and south side of Zhongyuan Road within Hongcaoyuan, Hongcao Town, Shanwei Urban District
Copyright© 2022 Guangdong Bao Jie Technology Co., Ltd.All Rights Reserved.


 EN
EN 





